
Converged Infrastructure
Customers have typically looked at Converged Infrastructure systems to provide integrated hardware platforms that will minimise risk and deployment times for an agile application environment. This can be based on the three main pillars of Converged Infrastructure systems, Compute, Storage and Network however in some cases this may also include a layer of automation and orchestration.
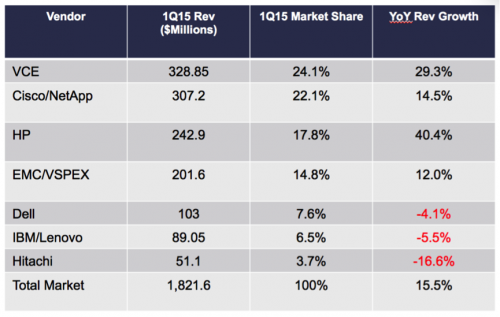
Converged Infrastructure solutions were first introduced in 2010 with adoption and IT spends increasing significantly over the last five years. Current IDC Market Share reports show the two predominant systems today are the VCE Vblock and the Cisco/NetApp Flexpod. Latest revenue and market share figures from publicly available data from IDC can be seen below:
Gartner have also been tracking the Converged Infrastructure market and recently have merged their reports to include Hyper-converged solutions.
Today there are two main approaches to Converged Infrastructure systems; the first being a fully engineered and pre-built solution that is assembled and configured in the factory then shipped shipped directly to the customer, a good example of this type of system is the VCE Vblock.
The VCE Vblock was first released into the market in 2010 and comprises Cisco Unified Computing System, Cisco Nexus Switching and EMC Storage, several models are available with each Vblock designed to support given levels of workloads or specific application environments. Should customers require expanding their environment this is typically addressed by adding a further Vblock?
The second option customers have, is the approach where the systems are based on validated designs that are built and tested in the vendor labs resulting in published reference architecture, this process reduces risk and deployment times when being provisioned by the customer or their IT provider.
Primary Use Cases:
The above solutions are typically deployed for delivering applications running within Virtualised Server environments inside customer data centres and now more frequently being deployed to deliver cloud solutions both on customer premises and at service provider locations offering IaaS services.
In many cases customers and service providers have deployed UCS Director (as described in previous blogs) as an automation/orchestration layer to provide the agility required in cloud environments whilst also further reducing deployment times.
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure is a more recent technology that in many cases is being viewed as an alternative to the Converged Infrastructure, so what is different and why are customers looking for an alternative?
Hyper-Converged systems also combine Compute Networking and Storage, however the storage is typically provided by local storage running on the compute platforms, therefore from this we can assume the use of Rack Servers. The local storage in the servers is then provisioned as a storage solution using Software Defined Storage software that can present storage to applications in a similar way to the traditional storage solutions seen in Converged Infrastructure systems.
Customers evaluating this technology are typically looking to reduce the cost of storage as many have seen their traditional storage solutions becoming cost prohibitive as storage requirements continue to increase. Cost reduction is a key consideration for both enterprise customers looking for a more cost effective way to deliver storage and also smaller customers that are looking to minimize complexity and cost.
A second important area of consideration is the ability to manage Compute, Network and Storage through a single management interface which some solutions deliver better than others.
There are currently many vendors and solutions available in the market today each with a slightly different definition and approach to Hyper-Converged, however I would expect as the market matures over the coming months and years that will see acquisitions in this space that will ultimately define the technology going forward.
Cisco’s current approach to Hyper-Converged solutions is to partner with the leading vendors in this space. There are several solutions available today utilising Cisco UCS Rack Servers for compute and storage along with Nexus switching platforms.
Cisco has jointly published reference architectures, datasheets and whitepapers based on the following partner solutions: Simplicity OmniStack, VMware VSAN, EMC ScaleIO, StorMagic SvSAN and Maxta MxSP.
Further Information on the above solutions can be found at the following URLs:
Primary Use Cases:
Customers looking to deploy a virtualized server environment comprising Compute, Network and Storage with integrated management.
Hyper-Converged solutions also appeal to SMB customers that do not need the capacity or complexity of traditional storage solutions and are also looking for backup and resilience from the solution.
A further target area for this type of solution is for customers that are looking to expand compute and storage independently as sometimes required in scaling environments.