
Security Tip of the Month: “Who and What to Trust?” Zero Trust – A Security Challenge for the New Era
2 min read
The current moment that we are living, the Covid-19 pandemic, has forced many companies around the world to suddenly move their entire workforce from working within the physical office to working from anywhere. This unplanned shift to remote connectivity for all workers significantly increases the security risk of any organization. In response, many organizations are now accelerating their efforts to implement Zero Trust.
What is Zero Trust? Zero Trust is a security framework created in 2009 by John Kindervag and centered on the belief that organizations shouldn’t trust something just because it’s on the inside of your firewall, you must verify anything and everything trying to connect to our systems before granting access.
Zero Trust Security helps organizations to implement dynamically security controls which are better prepared to handle this new reality of remote work. This approach abandons the notion of well-defined network perimeters and instead moves the perimeter for wherever access control decisions are made. This improves the organizational security posture and maturity, despite the growing attack surface brought by the increase of the remote workers during this pandemic period.
Generally speaking, Zero Trust mainly focus is on enforcing policies at the point of access, and take into account four key controls to implement the model, namely:
1. Least privileged
- Microsegmentation at the network layer;
- Authenticate first then allow connection.
2. Multi-factor authentication
- Creates an extra layer of security;
- Verify users’ identities, gain visibility, and enforce adaptative policies to secure access to every application.
3. Endpoint Security
- Check the endpoint at every authentication;
- Ensures devices comply with corporate security policy before allowing access;
- Bind the user directly to the device;
4. Monitoring Continuously
- Use analytics to ensure the users are authenticating as expected;
How to achieve a Zero Trust architecture with Cisco?
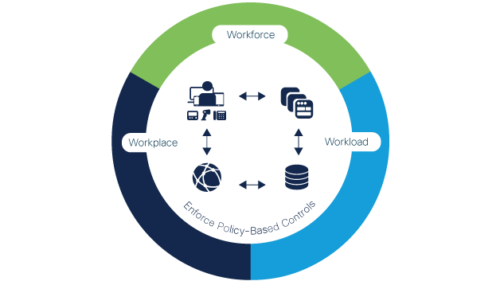 Cisco Zero Trust security framework helps organizations to prevent unauthorized access, contain breaches, and reduce the risk of an attacker’s lateral movement through your network.
Cisco Zero Trust security framework helps organizations to prevent unauthorized access, contain breaches, and reduce the risk of an attacker’s lateral movement through your network.
It allows organizations to consistently enforce policy-based controls, gain visibility into users and devices, components across entire network, get detailed logs, reports and alerts that can help security teams to better detect and respond to security threats.
Cisco has integrated solutions to address three major pillars of Zero Trust: the workforce, workload and workplace.
Duo protects the workforce – helping protect your users and their devices against stolen credentials, phishing, and other identity-based attacks. It verifies users’ identities and establishes device trust before granting access to applications.
Tetration protects workloads – securing your hybrid multicloud workloads and contain lateral movement with application segmentation. It gets complete visibility and determines the dependencies within databases and applications.
Software-Defined Access protects workplaces – gaining insight into users, devices and identify threats, maintaining control over all connections across your network, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices like cameras, manufacturing equipment, and more.
This complete zero-trust security model allows you to mitigate, detect and respond to risks across your environment.
Plan your strategy and prepare for Zero Trust adoption with Cisco!
